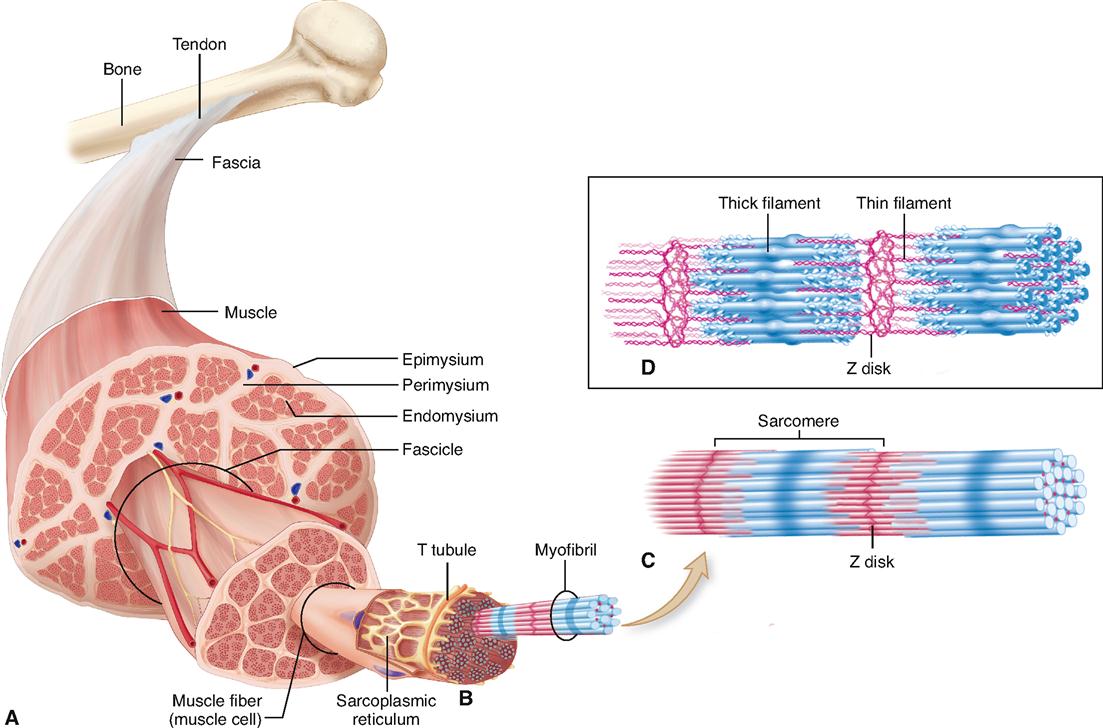
Describe the General Structure of a Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Using these criteria there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. It contains sacs of the neuro-transmitter acetylcholineACh.

Muscle Definition Function Types And Structure Biology Dictionary
fine and satellite cells from skeletal muscle have been structure of early functional contacts.
. The hierarchy of muscle structure can be seen in this representation of a typical vertebrate skeletal muscle. Slow oxidative SO fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration oxygen and glucose to produce ATP. In vitro development of skeletal muscle fiber.
Slow oxidative SO fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration oxygen and glucose to produce ATP. Describe the general structure of a skeletal muscle fiber. These invaginations allow depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate to the interior of the cell.
-Muscle cells are long cylindrical multinucleated -Sarcolemma muscle cell membrane-Sarcoplasm filled with tiny threads called myofibrils. A muscle fiber sometimes called a muscle cell is made up of hundreds or thousands of individual cylindrical muscle cells. In both injured and diseased states ECM adapts dramatically a property thathas clinical manifestations and alters muscle function.
The membrane of the muscle fiber is the sarcolemma which contains receptor sites for acetylcholine and an. Skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm 118 in in the Sartorius of the upper leg. Also it has muscle fibercitoplasm sarcoplasm which consists of a large number of mitochondria energy producers.
9 successfully engrafted into cardiac tissue of. These fascicules are cylindrical in shape as shown in the figure. Skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large compared to other cells with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm 118 in in the Sartorius of the upper leg.
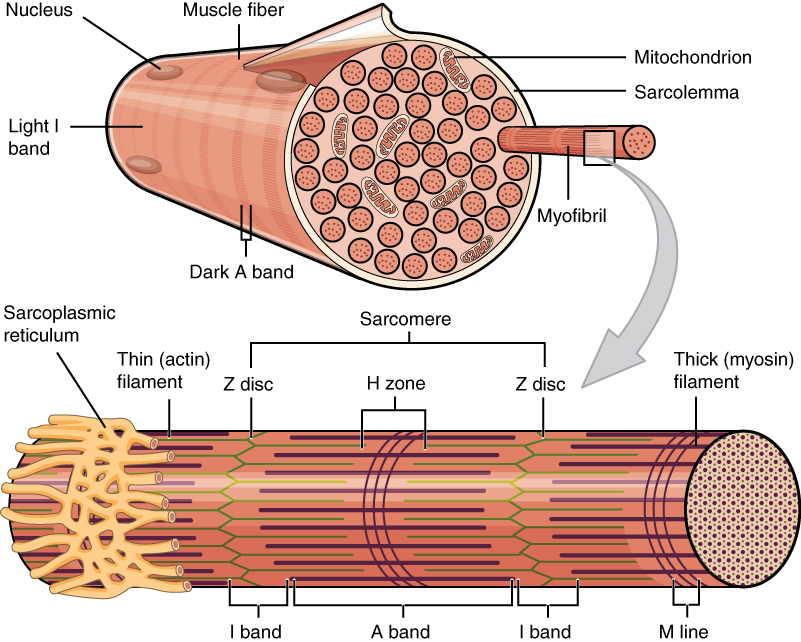
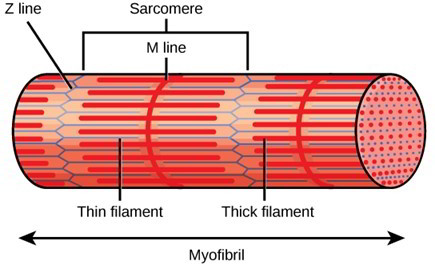
Skeletal muscle fibers are composed of a bundle of thin filaments called myofibrils. Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils long cylindrical structures that lie parallel to the muscle fiber. Describe the general structure of a skeletal muscle fiber.
The protocols given here describe basic steps to obtain aneural skeletal muscle cultures and should be used as a general guide. Muscle fiber also consists of sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse. They attach to the plasma membrane called the sarcolemma at their ends so that as myofibrils shorten the entire muscle cell contracts Figure 1618.
Skeletal muscle fiber type. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers or myofibers. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers.
Skeletal muscle fibers structure consists of sarcolemma which is a membrane of muscle fiber. Or connective tissue associated with a muscle form broad fibrous sheets called aponeuroses. Muscle fiber has contractile fibers called actin and myosin which form sarcomere.
The skeletal muscles consist of a bundle of muscle fibres namely fascicule. Having many nuclei allows for production of the large amounts of. This connective tissue surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the ends of its muscle fibers forming cordlike tendon.
The skeletal muscle extracellular matrix ECM plays an important role in muscle fiber force transmission maintenance and repair. The basic unit of. Individual muscle fibers with their contractile proteins organized into myofibrils with A-bands and I-bands and sarcomeres S defined by the Z-lines are innervated in a group muscle unit by a single motor axon forming a motor unit.
Structure of Skeletal Muscle Fiber. Each skeletal muscle fiber is a skeletal muscle cell. Myofibrils run the entire length of the muscle fiber.
Transverse tubules portion of the sarcoplasmic reticulum that stores and releases calcium during contraction and relaxation. The resulting multinucleated muscle fiber is a thin elongated cylinder with rounded ends that attach to the connective tissues associated with a. Each fiber forms from many undifferentiated cells that fuse during development.
Using these criteria there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber has its own motor nerve ending. The neuromuscular junction is where the motor neuron terminates on the muscle fiber Fig.
Using insights from muscle developmental biology to dissect targets for susceptibility and resistance to muscle disease. Skeletal muscles are so named because they are attached to bones by tendons and move these bones and the loads borne by them. Here we review the structure composition and mechanical properties of skeletal.
During early development embryonic myoblasts each with its. Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical and multinucleate. The axon terminal is the enlarged tip of the motor neuron.
During early development embryonic myoblasts each with its own nucleus fuse with up to. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook. They are 10 30 cm in length long enough to justify the term fiber.
Describe the general structure of a skeletal muscle fiber. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others and how fibers produce ATP.
Skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm 118 in in the Sartorius of the upper leg. Myoneural junction where motor nerve. Which is the plasma membrane of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle cells.
Solutions for Chapter 8 Problem 2P. Each myofibril is made up of small sections called sarcomeres. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers.
Sarcolemma membrane surrounding the muscle fiber. Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others and how fibers produce ATP. Start studying Structure of Skeletal Muscle Fiber.
101002wdev230 Zierath JR et al. Skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue called fascia. They are formed by fusion of several smaller cells into a multinucleate syncitium.
These muscle fibres are surrounded by blood vessels and a number of layers of other tissues enclosing it.
Physiology Of The Muscular System Basicmedical Key

Describe The Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Brainly In
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology

Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology I

Skeletal Muscle Consists Of Muscle Fibers Bound By Connective Tissue Download Scientific Diagram
What Is The Relationship Between Muscle Fibers Fascicles Myofibrils And Muscles From Largest Structure To Smallest Quora

Skeletal Muscle Veterinary Histology

Skeletal Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Muscular System Anatomy Muscle Tissue

Sarcoplasm An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Structure And Function Open Textbooks For Hong Kong

A Illustration Of Skeletal Muscle Structure Copied With Permission Download Scientific Diagram

The Basic Structure Of Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Is Made Up Of A Download Scientific Diagram
Structure Of Skeletal Muscle Earth S Lab

10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology

Muscle Fundamentals Components Characteristics And Contraction Mblex Guide

Skeletal Muscle Definition Function Britannica

Contraction In The Simplest Sense Is Shortening Of A Muscle Fibre When Muscles Receive Stimulation From The Ner Muscle Structure Muscle Diagram Muscle Anatomy

Comments
Post a Comment